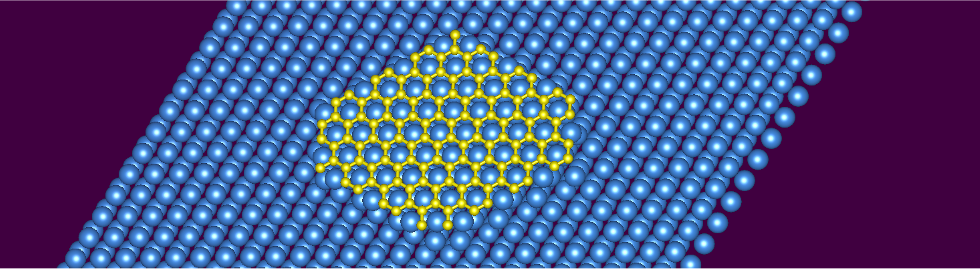
Scientists examined whether honeycomb boron can function as a structural analogue 2D material to graphene. Employing core-level X-ray spectroscopies, scanning tunneling microscopy, and DFT calculations, they analyzed the structure and electronic properties of honeycomb boron after its reaction with aluminum. They found that although it resembles graphene in electronic structure to some extent, it fails to form a quasi-freestanding monolayer on aluminum. This lack of a freestanding state is a clear difference from the behavior of graphene or monolayer hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) on lattice-mismatched metal surfaces.