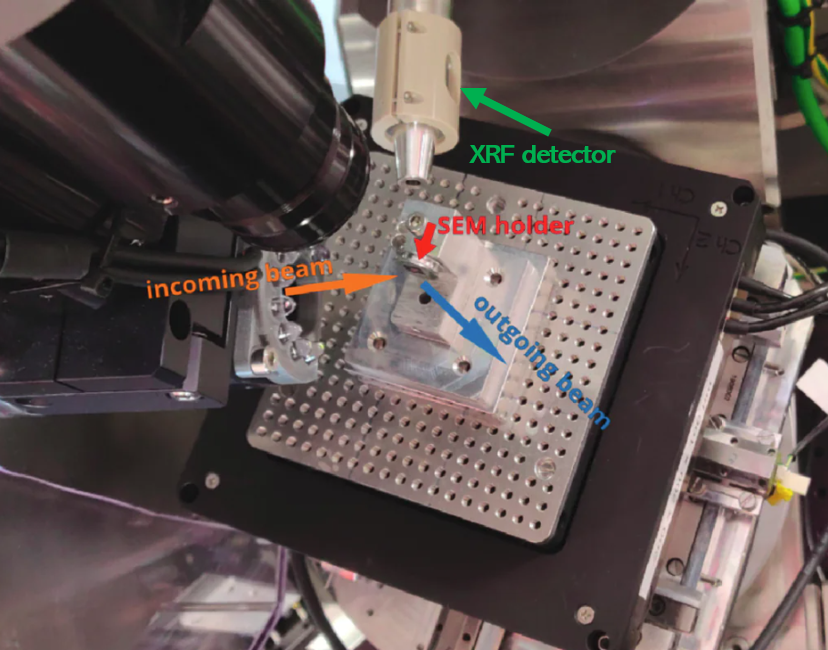
The Diffraction Station (EH2) has a coarse stage (+/- 10 mm) and piezo motors used for scanning that can cover a range of +/- 45 µm. Locating the region of interest on your sample can be tricky if the features are small, but there are a number of features of the EH2 that can aid in this process.
Microscopes
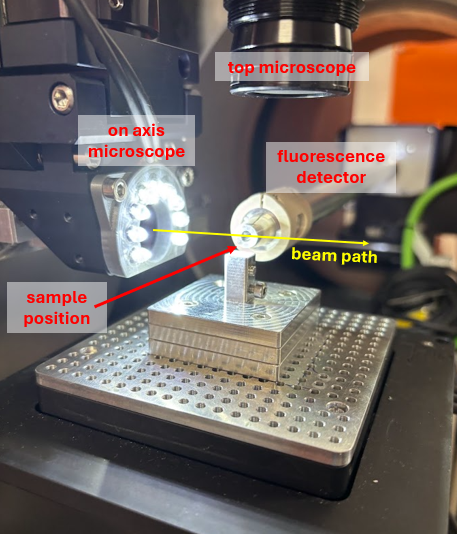
Two microscopes are mounted at EH2, the on-axis microscope (OAM) and top microscope (TOPM). The OAM looks in the same direction as the beam and has adjustable LED array. The TOPM looks from above the sample.
Both microscopes feature physical objectives (controlled by the beamline software) to image either a wide field of view or at higher resolution.
The OAM allows for viewing of your sample in the same direction as the X-ray beam. The position of the beam is marked on the microscope viewer to aid in alignment to the region of interest. If samples are rotated to high angles it may be challenging to view them in the OAM or TOPM, but alignment is usually still possible.
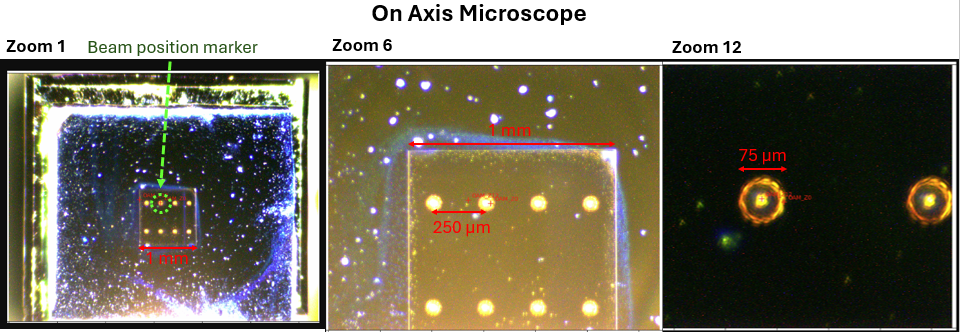
Below is an example of the field of view and resolution you can expect from the OAM.
Fluorescence
X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is powerful for quantitative chemical mapping and is used at both NanoMAX end stations. At the Diffraction station (EH2) it can also be a helpful alignment tool. If it is difficult to visually align with a sample, low-resolution, large field of view XRF mapping can be used to align to features of interest.
XRF alignment has a few requirements:
- Scanning is not feasible over areas larger than 100 µm. Some form of alignment (distance from sample edge, coarse features visible in the microscope, etc) are still needed for alignment.
- XRF will only be sensitive to elements with X-ray absorption edges below the photon energy, as such you may need to choose the photon energy accordingly. Please see the X-ray fluorescence page for more information or talk to the beamline staff if you have any questions.
- For thick samples (>10 µm) to be measured in reflection mode for diffraction, the fluorescence detector is located behind the sample (see below), therefore fluorescence will not be accessible.
- It may be an option to locate the region of interest, then rotate the sample to the required diffraction angle.